Emotet Employs New Lures in Recent Campaign
Garden State Cyber Threat Highlight
Original Release Date: 10/22/2020
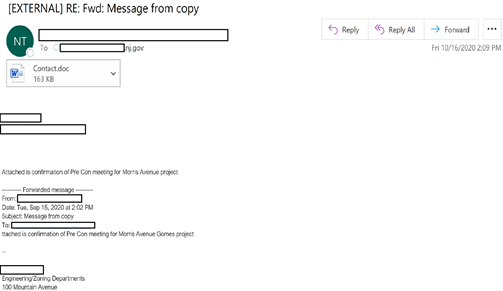
Image: Example Emotet Email Sent to NJ State Employee
The threat actors behind Emotet continue to evolve their tactics and themes in its new email phishing campaign. Emotet campaigns dominated the top malware-laden emails attempting to be delivered to New Jersey state employees over the last 30 days, encompassing six of the top ten campaigns. Recently, the trojan is spreading via malicious Word and Excel document attachments or links leading to attachments delivered with emails referencing an invoice or work-related matter, COVID-19, or the president’s health. When opened, the documents display a message informing the user they need to Enable Editing and Enable Macros in order for the document to display. If the user enables macros to run, Emotet is installed on the user’s system. Emotet is a sophisticated trojan used to install additional malware onto infected systems, including the TrickBot trojan and Ryuk ransomware. TrickBot has extensive capabilities on its own, which include quickly spreading across a network and stealing credentials, system information, and other sensitive data. Microsoft and others have been attempting a takedown of the TrickBot botnet in recent weeks in hopes to cripple threat actors’ operations. Microsoft’s attempts to dismantle TrickBot’s infrastructure may lead to threat actors’ use of Emotet’s infrastructure to continue their operations. Ryuk, often dropped via Emotet and TrickBot, is one of the most advanced and prevalent ransomware variants and averages over one million dollars in ransom per victim, with overall costs of remediation significantly raising losses. Recent increases in Emotet activity targeting state and local governments was detailed in a CISA alert earlier this month.
Recommendations
The NJCCIC recommends prioritizing awareness of the tactics used in Emotet campaigns to prevent victimization. We reminds users to exercise caution when clicking on links or opening attachments sent in emails from both trusted and unknown entities, verify the legitimacy of requests via a separate means of communication, and avoid enabling macros in documents unless there is a known use for this feature. If an Emotet infection is suspected, we recommend disconnecting devices from the network and investigating them for signs of compromise, reimaging any systems that are determined to be infected. Additionally, we urge organizations to implement a defense-in-depth cybersecurity strategy that includes an endpoint detection and response solution, email security gateway, user awareness training, and a comprehensive data backup plan.